As we age through life, our nutritional needs evolve, especially with changes to our needs and activities. It’s a natural process, but one that demands our attention, focus, and informed choices. In this article, we will delve into the key nutritional risk factors faced by aging adults and explore the five essential nutrients they need for a healthy life. We’ll also discuss the difference between getting nutrients from food versus dietary supplements and provide practical options for nutritional strategies in promoting well-being in the later years. Let’s embark on this journey of nourishment and empowerment of informed choices.
Risk Factors Faced With Aging Adults
Aging is a natural and beautiful part of life, but it also comes with certain nutritional challenges that can impact our overall health and well-being. Understanding these challenges and staying informed is the first step toward addressing them effectively. Here, we’ll take a deeper look at the three prominent nutrition risk factors that aging adults often encounter.
Decreased Appetite:
One of the most noticeable changes in dietary habits as we age is a decreased appetite which can be attributed to a decrease in our activities. There are several reasons behind this phenomenon:
The consequence of a decreased appetite is a potential reduction in the intake of essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals. Over time, this can lead to malnutrition, muscle loss, and a weakened immune system, which can increase the risk of illness and decrease overall quality of life.
- Changes in Metabolism: As we get older, our metabolism tends to slow down. This means our bodies require fewer calories to maintain our current weight. As a result, we may not feel as hungry as we used to.
- Loss of Taste and Smell: Aging can lead to a diminished sense of taste and smell, making food less enjoyable especially if we are not open new food choices. When food doesn’t taste or smell as appealing, it can contribute to a reduced desire to eat.
- Medications: Many older adults take medications for various health conditions, and some of these medications can affect appetite. These medications can cause side effects like nausea or have a negative effect in taste perception.
- Chronic Health Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and cancer can impact appetite. Managing these conditions may require dietary restrictions that affect the types and amounts of food an individual.
5-Key Nutrients Needed For Aging Adults

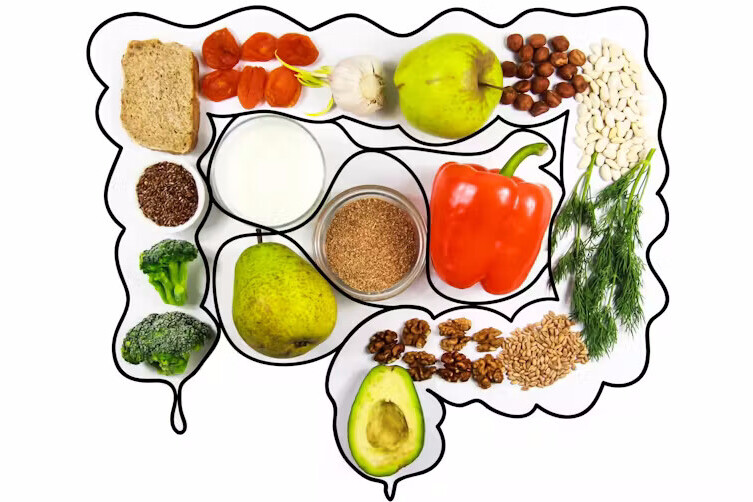
To address the nutritional challenges of aging successfully, it’s essential to focus on five key nutrients that play a vital role in maintaining health and vitality:
- Calcium and Vitamin D: These are crucial for bone health and can help prevent osteoporosis. Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods are excellent sources.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish like salmon and walnuts, omega-3s support brain health and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Fiber: A diet rich in fiber aids digestion, helps manage weight, and lowers the risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are great sources.
- Antioxidants: Vitamins C and E, along with other antioxidants, help protect cells from damage and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Berries, nuts, and colorful vegetables are packed with these nutrients.
- Protein: Adequate protein intake is essential for maintaining muscle mass, immune function, and overall strength. Lean meats, dairy, legumes, and plant-based sources like tofu are excellent options.
Nutrients Through Food vs. Dietary Supplements
While dietary supplements can be valuable tool, it’s crucial to prioritize getting nutrients from whole foods whenever possible. Here’s why:
- Synergy: Whole foods contain a complex mix of nutrients that work synergistic ally to promote health. Supplements can’t replicate this synergy.
- Natural Foods: Nutrients from food are often better absorbed than those from supplements, thanks to the natural packaging of nutrients in food.
- Safety: Some supplements can interact with medications or have adverse effects if taken in excess. Whole foods rarely present such risks.
However, supplements can be invaluable to filling gaps in your diet when advised by a healthcare professional. They are not a substitute for a balanced diet but can complement it.
Nutritional Strategies For Older Adults

- Small, Frequent Meals:As mentioned earlier, decreased appetite is a common issue among older adults. To counter this, consider shifting from the traditional three large meals a day to smaller, more frequent meals and snacks. This approach can make it easier to meet your nutritional requirements without feeling overwhelmed by large portions. It also helps stabilize blood sugar levels throughout the day, providing a steadier source of energy.
- Hydration:Staying hydrated becomes increasingly critical with age. Older adults may have a reduced sense of thirst, making it easier to become dehydrated. Dehydration can lead to a range of health issues, including urinary tract infections, kidney problems, and confusion. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water daily, and consider incorporating hydrating foods like water-rich fruits and vegetables into your diet.
- Consult a Dietitian:Consulting with a registered dietitian can be incredibly beneficial, especially if you have specific dietary concerns or medical conditions. A dietitian can assess your individual needs and create a personalized nutrition plan tailored to your preferences and requirements. They can also provide guidance on managing chronic health conditions through dietary choices.
- Mindful Eating:Mindful eating involves paying close attention to your body’s hunger and fullness cues. As we age, our metabolism and appetite can change, making it important to eat when you’re genuinely hungry and stop when you’re comfortably satisfied. Avoid rushing through meals and take the time to savor the flavors and textures of your food. Mindful eating can help prevent overeating or under eating, promoting a healthier relationship with food.
- Stay Active:Regular physical activity remains a crucial component of overall health, even as you age. Exercise helps maintain muscle mass, bone density, and cardiovascular health. It can also stimulate your appetite and improve digestion. Engaging in activities you enjoy, such as walking, swimming, or yoga, can make it easier to stay active as you get older.Additionally, consider incorporating strength training exercises into your routine to preserve muscle mass and strength. Consult with a fitness professional or physical therapist to design a safe and effective exercise program tailored to your needs and abilities.
Conclusion
As you age, prioritizing proper nutrition becomes increasingly important for maintaining a high quality of life. By adapting your eating habits to address specific challenges like decreased appetite and staying hydrated, consulting with a dietitian, practicing mindful eating, and staying active, you can promote your overall well-being and enjoy your golden years to the fullest. Remember that it’s never too late to make positive changes to support your health and vitality as you age.