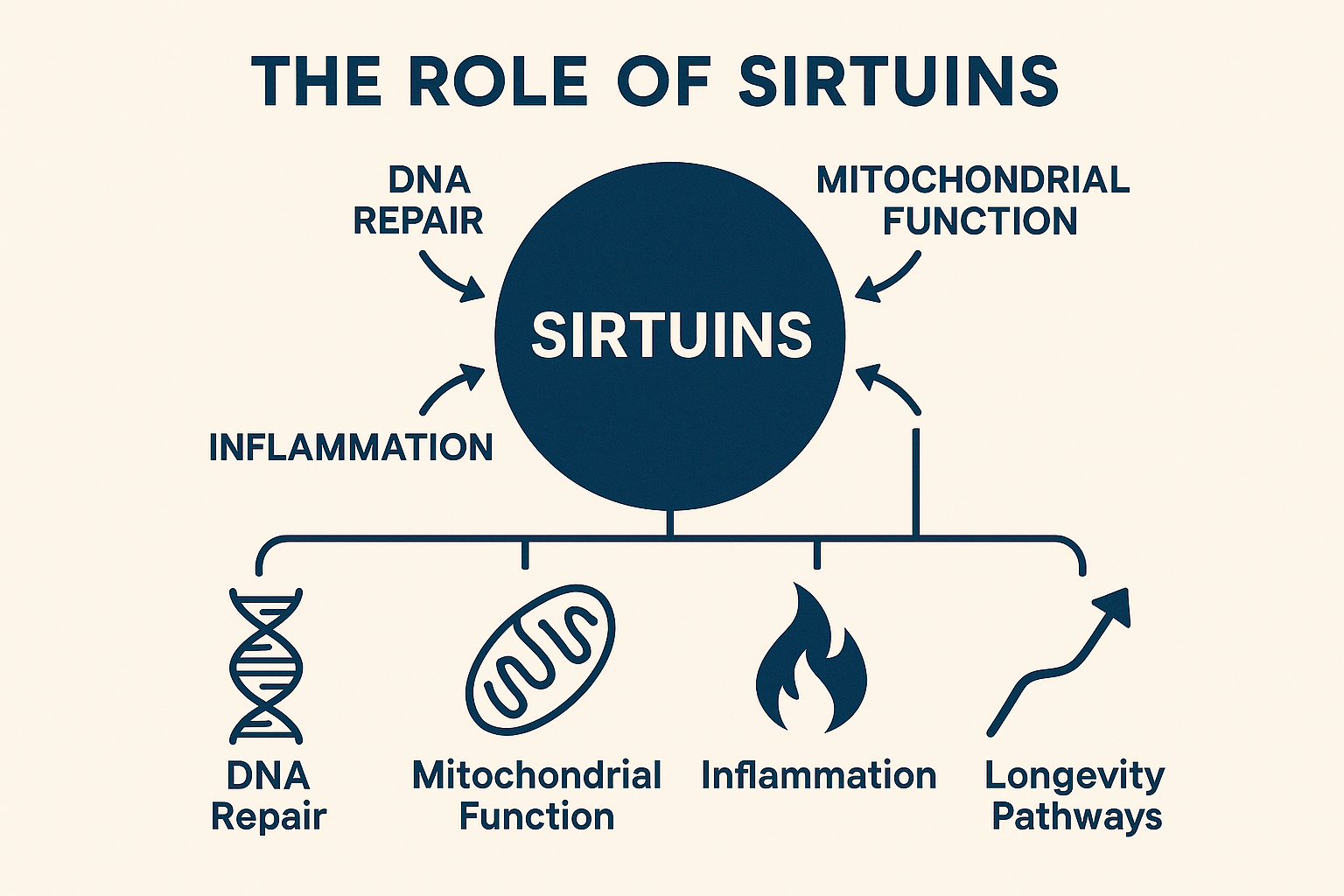
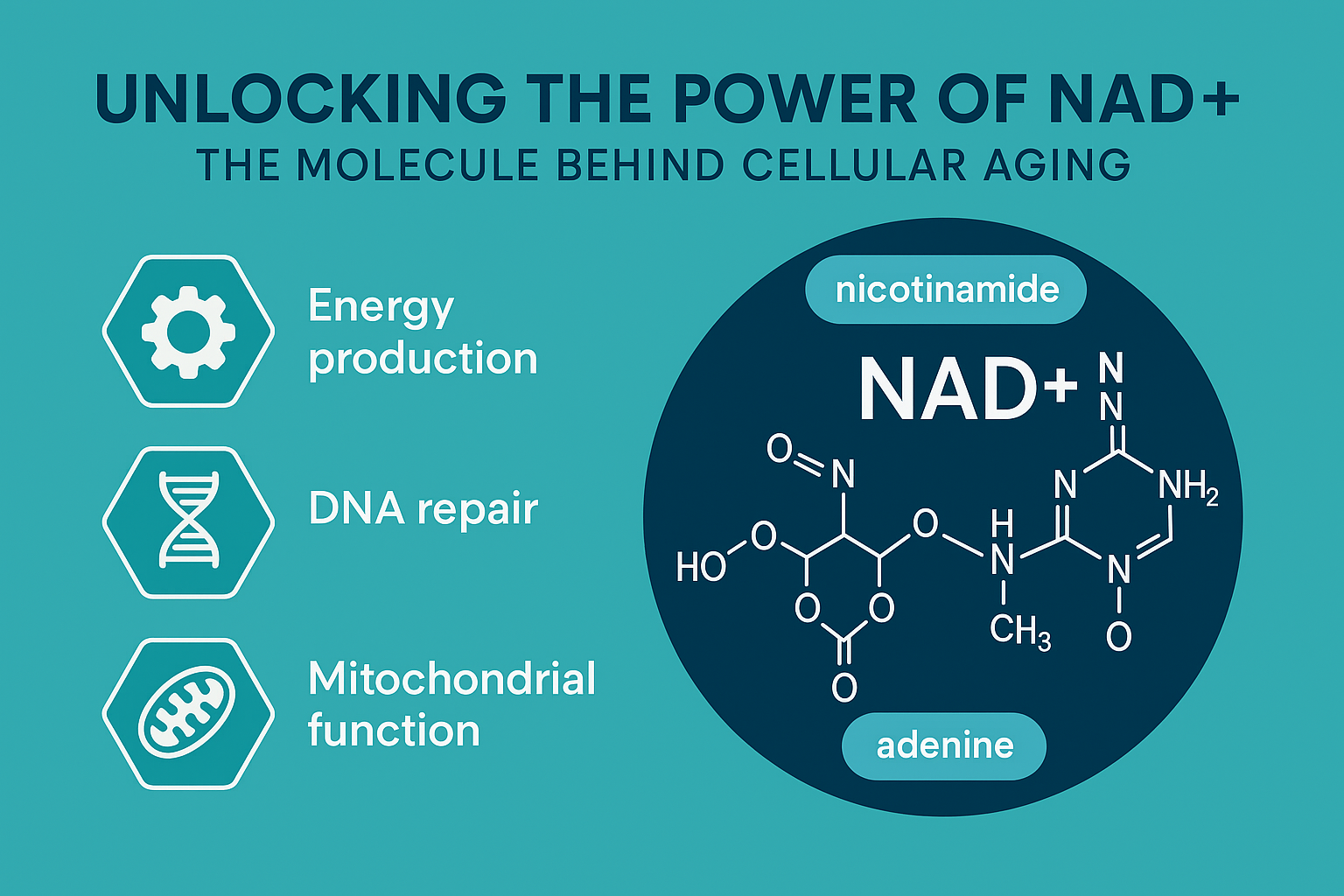
Imagine waking up each day feeling more energetic, youthful, and vibrant—not just in your mind, but in your body as well. What if the secret to achieving this lies in an unexpected place: your gut?
Gut health has emerged as a crucial factor in determining our overall well-being, especially as we age. A growing body of research underscores the intricate connection between our digestive system and the aging process. Let’s explore how maintaining a healthy gut can influence aging, promote longevity, and enhance quality of life.
Understanding Gut Health and Its Role in Aging
The gut, often referred to as the “second brain,” houses a complex community of trillions of microorganisms known as the microbiome. These bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes play a pivotal role in digestion, immune function, and even mental health. As we age, the composition and diversity of our gut microbiome tend to change, often leading to a decline in gut health.

Key Factors Affecting Gut Health in Aging:
- Dietary Changes: Aging often brings about changes in dietary habits, which can impact the microbiome. Reduced fiber intake, increased consumption of processed foods, and decreased appetite can all contribute to an imbalance in gut bacteria.
- Medications: Older adults are more likely to take medications, including antibiotics, that can disrupt the microbiome. These medications can kill beneficial bacteria, leading to dysbiosis, an imbalance in the gut microbiota.
- Reduced Physical Activity: Regular exercise is known to promote gut health by enhancing the diversity of the microbiome. However, physical activity levels often decrease with age, potentially affecting gut health negatively.
- Immune System Changes: The immune system weakens with age, making it less effective at maintaining a healthy balance of gut bacteria. This can lead to an increase in harmful bacteria and a decrease in beneficial ones.
- Chronic Diseases: Conditions such as diabetes, obesity, and inflammatory diseases are more prevalent in older adults and can significantly impact gut health.
How Gut Health Influences Aging
1. Inflammation
Inflammation is a natural immune response to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation, often referred to as “inflammaging,” is a persistent, low-grade inflammation associated with aging. This chronic state of inflammation is linked to many age-related diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, arthritis, and Alzheimer’s disease.
- Role of Gut Health: A healthy gut microbiome can help regulate inflammation. Beneficial bacteria produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as butyrate, propionate, and acetate, which have anti-inflammatory properties. These SCFAs help maintain the integrity of the gut lining, preventing the leakage of harmful substances into the bloodstream that can trigger systemic inflammation.
- Impact of Dysbiosis: When the gut microbiome is imbalanced (dysbiosis), harmful bacteria can proliferate, producing pro-inflammatory compounds. This can lead to increased intestinal permeability (“leaky gut”), allowing endotoxins to enter the bloodstream and promote chronic inflammation.
2. Immune Function
A significant portion of the immune system resides in the gut, where it interacts closely with the gut microbiota. This interaction is essential for maintaining a balanced and effective immune response.
- Role of Gut Health: A healthy microbiome helps train the immune system to distinguish between harmful pathogens and harmless or beneficial microbes. This education process is critical for preventing autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues.
- Impact of Dysbiosis: Dysbiosis can disrupt this training process, leading to an overactive immune response or a weakened immune system. This can result in increased susceptibility to infections, slower recovery from illnesses, and a higher risk of autoimmune diseases.
3. Cognitive Health
The gut-brain axis is a complex communication network that links the gut and the brain. This connection plays a vital role in regulating mood, cognition, and overall brain health.
- Role of Gut Health: Beneficial gut bacteria produce neurotransmitters (such as serotonin and dopamine) and other metabolites that influence brain function. They also help modulate the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that supports the growth and survival of neurons.
- Impact of Dysbiosis: An imbalanced microbiome can produce neurotoxic substances and promote systemic inflammation, which can negatively impact brain health. Dysbiosis has been linked to various neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and depression.
4. Nutrient Absorption
Efficient digestion and nutrient absorption are essential for maintaining energy levels, supporting bone health, and promoting overall vitality, especially as we age.
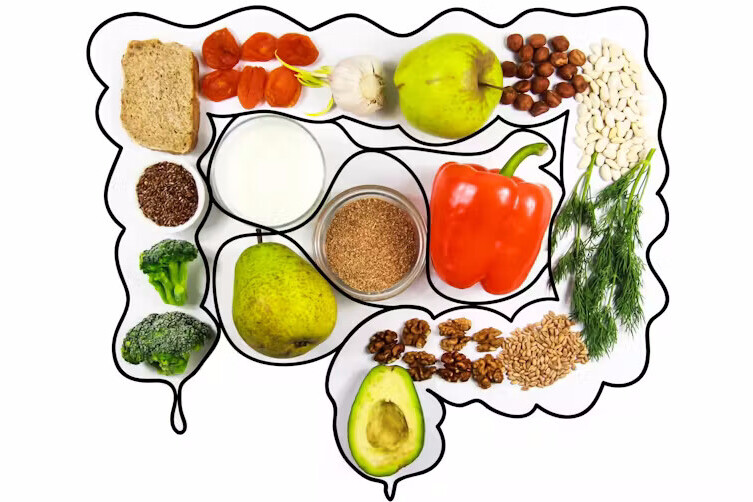
- Role of Gut Health: A balanced microbiome aids in the breakdown of food and the absorption of vital nutrients, including vitamins (such as B12 and K), minerals (such as calcium and magnesium), and amino acids. These nutrients are crucial for maintaining healthy bones, muscles, and cognitive function.
- Impact of Dysbiosis: Dysbiosis can lead to malabsorption of nutrients, resulting in deficiencies that can affect overall health. For example, a lack of vitamin B12 can lead to anemia and neurological issues, while calcium deficiency can contribute to osteoporosis.
5. Skin Health
The state of our gut health is often reflected in our skin. An imbalanced microbiome can lead to skin issues such as eczema, acne, and premature aging.
- Role of Gut Health: A healthy gut microbiome supports skin health by regulating inflammation and maintaining the integrity of the skin barrier. Beneficial bacteria produce SCFAs and other metabolites that nourish the skin and protect against pathogens.
- Impact of Dysbiosis: Dysbiosis can lead to increased gut permeability, allowing inflammatory molecules to enter the bloodstream and affect the skin. This can result in various skin conditions, including eczema, psoriasis, and premature wrinkles.
Recommendations for Maintaining Gut Health as You Age

- Eat a Balanced Diet: Incorporate a variety of fiber-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, to nourish the beneficial bacteria in your gut. Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi are excellent sources of probiotics.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water aids in digestion and helps maintain the mucosal lining of the intestines, supporting a healthy gut environment.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in regular physical activity to enhance gut motility and promote a diverse microbiome. Activities like walking, swimming, and yoga are great options for older adults.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact gut health. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness to support a healthy gut-brain connection.
- Consider Probiotic Supplements: Probiotic supplements can help replenish beneficial bacteria in the gut. Look for high-quality supplements with a variety of strains and a high CFU (colony-forming unit) count.
Highly Rated Gut Supplements for Aging Adults
To further support gut health, here are three highly rated probiotic supplements, each with over 4-star ratings and positive reviews:
Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics for Women & Men
Why It’s Beneficial:
- Diverse Strain Profile: This supplement contains 50 billion CFUs and 16 probiotic strains, offering a broad spectrum of beneficial bacteria to support digestive and immune health.
- Prebiotics Included: Prebiotics are fibers that feed the beneficial bacteria in the gut, helping them thrive and multiply.
- Shelf-Stable: No refrigeration is needed, making it convenient for daily use.
Customer Reviews:
- Users report significant improvements in digestive health, reduced bloating, and enhanced overall well-being. Many appreciate the inclusion of prebiotics and the high potency of the formula.
Renew Life Ultimate Flora Probiotic
Why It’s Beneficial:
- High Potency: With 50 billion live cultures and 12 probiotic strains, this supplement is designed to support optimal digestive health and immune function.
- Delayed-Release Capsules: These capsules are formulated to survive stomach acid, ensuring that the probiotics reach the intestines where they are most needed.
- Non-GMO and Gluten-Free: This product is suitable for those with dietary restrictions.
Customer Reviews:
- Reviewers highlight the supplement’s effectiveness in improving gut health, alleviating digestive discomfort, and enhancing regularity. The delayed-release feature is particularly appreciated for its targeted delivery.
Why It’s Beneficial:
- Clinically Studied Strain: Align contains Bifidobacterium 35624, a unique and well-researched strain that has been shown to support digestive health.
- Consistency: Recommended by gastroenterologists, Align is known for its consistent quality and effectiveness.
- Convenient Daily Capsule: Easy to incorporate into a daily routine, this supplement supports ongoing digestive health.
Customer Reviews:
- Users praise Align for its reliability and effectiveness in maintaining digestive balance. Many report improvements in bloating, regularity, and overall gut health.
Conclusion
As we age, maintaining a healthy gut becomes increasingly important for overall well-being. A balanced microbiome can help regulate inflammation, support immune function, enhance cognitive health, improve nutrient absorption, and promote radiant skin. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits and considering high-quality probiotic supplements, we can support our gut health and age gracefully.
Investing in our gut health is investing in our future. The steps we take today to nurture our microbiome can lead to a healthier, more vibrant tomorrow. So, why not start now? Embrace the power of a healthy gut and unlock the secrets to aging well.
Disclaimer: Some of the links displayed may be affiliate links, which means that if you click on the affiliate link, I may receive a small commission. The commission is paid by the retailers and at no cost to you which helps to support this site/channel with the growing content. Thank you! In addition, I am not a medical professional. Ideas presented in this article are for entertainment and informational purposes only. Please do your own due diligence and seek medical advice from a licensed healthcare professional before starting any new regimen, diets, supplements, or programs to ensure it is safe and suitable for your individual health needs and circumstances. No material on this video is intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health care provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment.